WHAT IS SUSTAINABLE MICE?
WHAT IS SUSTAINABLE MICE?
Recently, the terms ‘Sustainable Development’ and ‘ESG’ have been key topics of interest.
The term Sustainable Development was coined in the 1987 report by the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), titled, “Our Common Future”, as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”.
‘ESG’ is a term derived from the initials of Environment, Social, and Governance. Recently, the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism and the National Institute of the Korean Language have selected ‘Environment, Social, and Transparent Management' as alternative terms. ESG means in order for a company to sustain and develop in the long term, it should focus not only on the financial perspective, but also consider non-financial factors, which include the perspectives of various stakeholders related to the company.
Within the MICE industry as well, the importance of Sustainability and ESG have increased, as its implementation in MICE events have proven to have significant impact on the venue. As social issues such as human rights, regional development and fair trade are added to Green MICE, a rapid growth and shift towards Sustainable MICE is taking place.
Summing up the above definitions, Sustainable MICE can be defined as “the concept of achieving sustainability in environmental, social and economic aspects through efficient resource management and stakeholder engagement.” It can be defined as a tool that evaluates the risks and materiality of non-financial factors in the environment, social, and governance aspects of MICE events for future application and development.
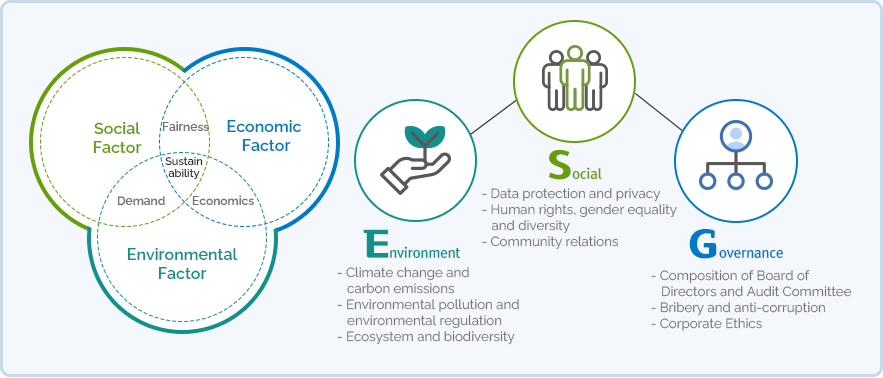
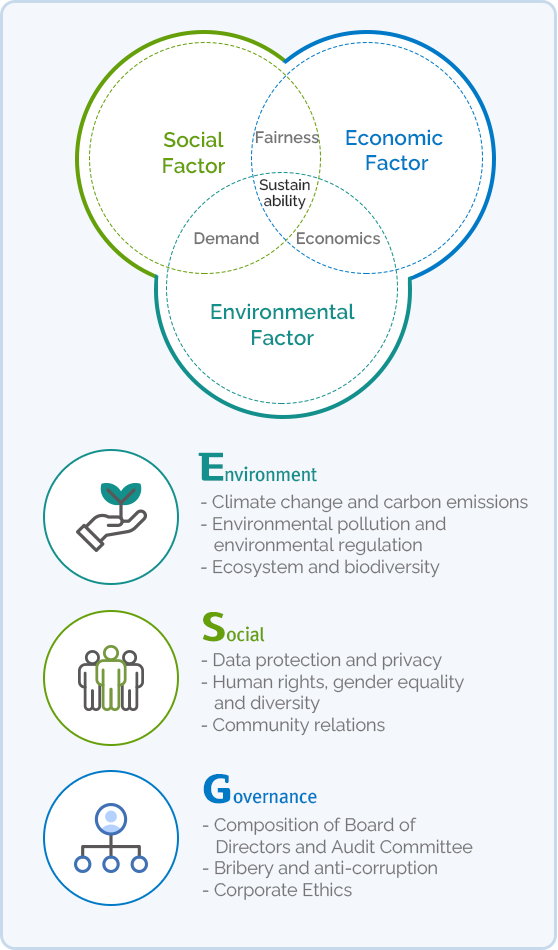
- Social Factor
- Fairness, Demand, Sustainability
- Economic Factor
- Fairness, Economics, Sustainability
- Environmental Factor
- Demand, Economics, Sustainability
Intersection of Social/Economic Factors: Fairness, Sustainability
Intersection of Social/Environmental Factors: Demand, Sustainability
Intersection of Economic/Environmental Factors: Economics, Sustainability
Intersection of Social/Economic/Environmental Factors: Sustainability
- Environment
- - Climate change and carbon emissions
- - Environmental pollution and environmental regulation
- - Ecosystem and biodiversity
- Social
- - Data protection and privacy
- - Human rights, gender equality and diversity
- - Community relations
- Governance
- - Composition of Board of Directors and Audit Committee
- - Bribery and anti-corruption
- - Corporate Ethics